Antonio Manaytay – Fourth Estate Contributor
Chapel Hill, NC, United States (4E) – The authentic pigment, beta-keratin and muscle proteins from a sea turtle hatchling that lived through the Eocene interval had established that the survival trait of contemporary sea turtles developed at the least 54 million years in the past.
The researchers from North Carolina University, Lund University in Sweden, and the University of Hyogo in Japan stated the persistence of the unique molecules for hundreds of thousands of years clearly confirmed that the pigmentation of the traditional specimen is shared with its trendy counterpart.
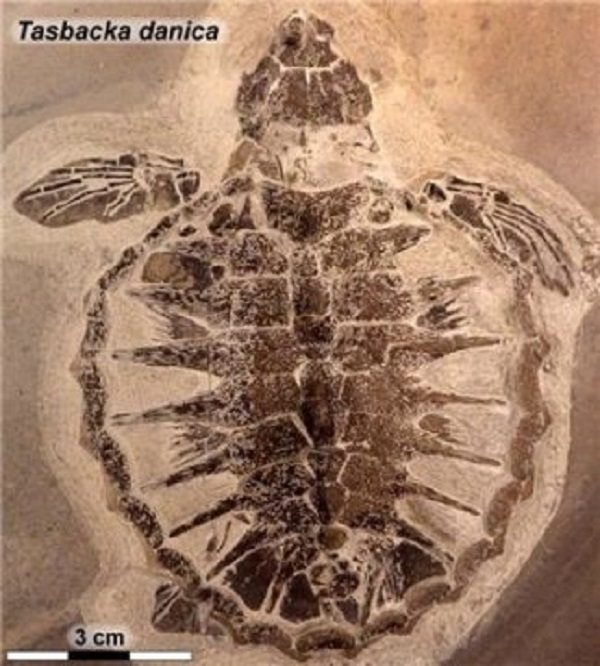
A well-preserved sea turtle hatchling, a Tasbacka Danica species, was present in 2008 from the Fur formation in Jutland, Denmark. The specimen, lower than three inches (74 millimeters) lengthy, was among the many sea turtles that lived between 56 and 34 million years in the past.
In 2013, paleontologist Johan Lindgren of Lund University had found some comfortable tissue residues close to the specimen’s left shoulder, from which he collected 5 samples for biomolecular evaluation.
Lindgren famous that the fashionable sea turtle hatchlings have dark-colored shells. This serves because the protecting mechanism from predators reminiscent of seagulls when they’re on the ocean floor. This darkish coloration additionally permits the cold-blooded sea turtle to soak up warmth from daylight to control physique temperature, which additionally permits them to develop at sooner fee. The historic specimen appeared to have shared this attribute.
The researchers have additionally famous that the spherical organelles discovered within the fossil are accountable for the ocean turtle’s darkish shade.
Lindgren had subjected the collected comfortable tissues to assessments to find out if the specimen had a darkish coloured shell. The methods used to check the specimen embody subject emission gun scanning electron microscopy (FEG-SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), in situ immunohistochemistry time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometry (ToF-SIMS), and infrared (IR) microspectroscopy.
Lindgren used the ToF-SIMS approach to substantiate the presence of heme, eumelanin, and proteinaceous molecules, that are the part of blood, pigment, and protein.
Study co-author Mary Schweitzer, then again, carried out histochemical evaluation on the pattern. She discovered that the pattern comprises antibodies for each alpha and beta-keratin, hemoglobin and tropomyosin.
The different researchers additionally carried out the assessments on the pattern: University of Hyogo evolutionary biologist Takeo Kuriyama carried out the TEM, and Schweitzer did the immunogold take a look at. The outcomes of all of the assessments carried out additional confirmed the findings.
All the proof gathered from the totally different assessments confirmed that these molecules are authentic to the specimen. The outcomes, in response to the researchers, had confirmed that these historic sea turtles and their modern-day counterparts have shared a pigmentation-based survival trait.
“The presence of eukaryotic melanin within a melanosome embedded in a keratin matrix rules out contamination by microbes because microbes cannot make eukaryotic melanin or keratin,” Schweitzer stated.
The findings clearly confirmed that the traditional specimen had dark-colored shell frequent to trendy sea turtles, she stated.
Article – All Rights Reserved.
Provided by FeedSyndicate