Arthur J. Villasanta – Fourth Estate Contributor
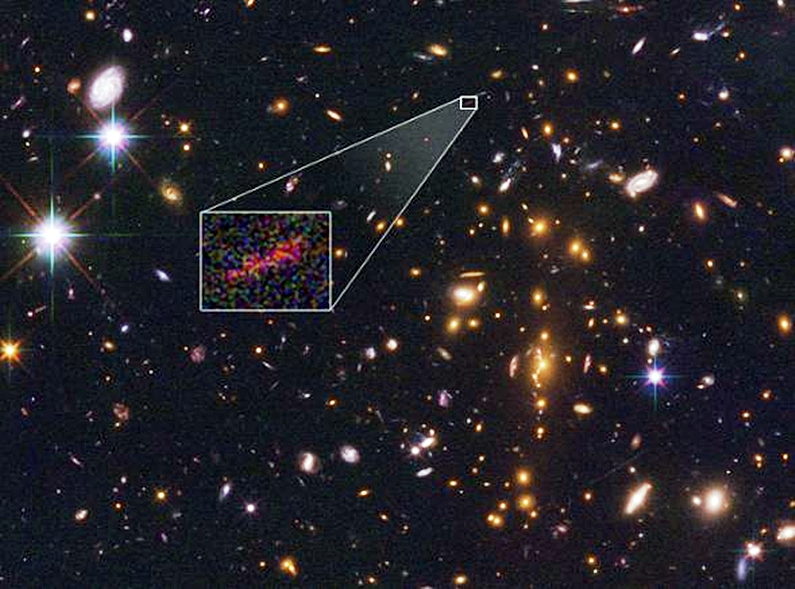
Washington, DC, United States (4E) – An intensive survey deep into the universe by NASA’s Hubble and Spitzer house telescopes has found the farthest galaxy but seen. The picture of this embryonic galaxy named SPT0615-JD has been stretched and amplified by a phenomenon known as gravitational lensing.
NASA mentioned SPT0615-JD existed when the universe was solely 500 million years outdated. The gravitational subject of a large foreground galaxy cluster amplified the sunshine from the background galaxy and in addition smeared the picture of it into an arc about two arcseconds lengthy.
SPT0615-JD was recognized in Hubble’s Reionization Lensing Cluster Survey (RELICS) and companion S-RELICS Spitzer program.
By combining the Hubble and Spitzer information, astronomers calculated the “lookback time” to the galaxy of 13.three billion years. Preliminary evaluation suggests the puny galaxy weighs in at not more than three billion photo voltaic lots (roughly 1/100th the mass of our absolutely grown Milky Way galaxy).
SPT0615-JD is lower than 2,500 light-years throughout, half the dimensions of the Small Magellanic Cloud (a satellite tv for pc galaxy of our Milky Way). The object is taken into account prototypical of younger galaxies that emerged in the course of the epoch shortly after the Big Bang.
“No other candidate galaxy has been found at such a great distance that also gives you the spatial information that this arc image does,” mentioned research lead writer Brett Salmon of the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore, Maryland.
“By analyzing the effects of gravitational lensing on the image of this galaxy, we can determine its actual size and shape.”
“RELICS was designed to discover distant galaxies like these that are magnified brightly enough for detailed study,” mentioned Dan Coe, Principal Investigator of RELICS.
RELICS noticed 41 large galaxy clusters for the primary time within the infrared with Hubble to seek for such distant lensed galaxies. One of those clusters was SPT-CL J0615-5746, which Salmon analyzed to make this discovery.
Upon discovering the lens-arc, Salmon thought, “Oh, wow! I think we’re on to something!”
The galaxy is correct on the limits of Hubble’s detection capabilities, however only the start for the upcoming NASA James Webb Space Telescope’s highly effective capabilities, mentioned Salmon.
“This galaxy is an exciting target for science with the Webb telescope as it offers the unique opportunity for resolving stellar populations in the very early universe.”
Article – All Rights Reserved.
Provided by FeedSyndicate