Arthur J. Villasanta – Fourth Estate Contributor
Atlanta, GA, United States (4E) – The number of persons in the United States infected with the three most common sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) has hit a record high in 2016, continuing a dismal trend that shows few signs of abating without urgent action.
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) in its recently released “Sexually Transmitted Disease Surveillance Report” said the three leading forms of STD in the country remain Chlamydia, gonorrhea and syphilis.
It reported more than two million new diagnoses for these three forms of STD in 2016. CDC estimates there are 20 million new notifiable and nonnotifiable STD cases every year in the U.S. Half of these occur in people 15 to 24 years old.
“STDs are a persistent enemy, growing in number, and outpacing our ability to respond,” said Dr. Jonathan Mermin, MD, MPH, director of CDC’s National Center for HIV/AIDS, Viral Hepatitis, STD, and TB Prevention.
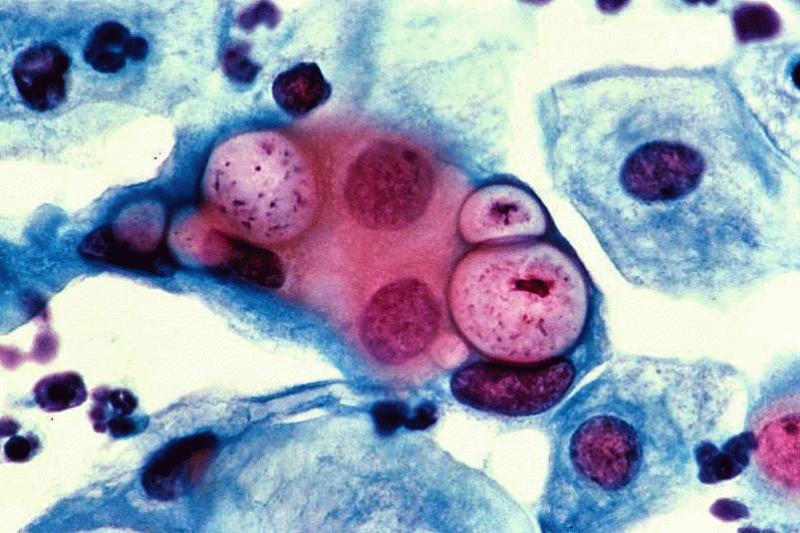
Chlamydia, a bacterial infection that affects the penis, vagina, cervix, anus, urethra, eyes and throat, accounted for most of the increase, with 1,598,354 new cases (497.3 cases per 100,000 population). The total for 2016 was a 4.7% increase over 2015.
Gonorrhea accounted for 468,514 diagnoses while primary and secondary syphilis (the most infectious stages of the disease,) had 27,814 cases.
Disturbing increases in syphilis and gonorrhea show the two diseases are infecting new populations.
Syphilis rates were up nearly 17.6% from 2015 to 2016, rising to 8.7 cases per 100,000 population.
Most (nearly 90%) of the cases occurred among men, especially men who have sex with men (MSM). The largest increases, however, were seen among women and infants. There was a 35.7% jump in syphilis rates in women and a 27.6% increase in congenital syphilis in 2016.
This spike represents “a tragic systems failure,” said Dr. Gail Bolan, MD, director of the CDC’s Division of STD Prevention.
In 2016, 628 cases of congenital syphilis were reported, resulting in 40 deaths and severe complications. There were 492 cases reported in 2015.
The rate of gonorrhea infections was 145.8 cases per 100,000, which was an overall increase of 18.5% over 2015. The largest increase was seen among men (up 22.2%).
The report authors note that research suggests a large proportion of these are found in MSM. Among women, there was a 13.8% increase during the same period.
Growth in the number of gonorrhea victims is particularly troubling because antibiotic resistance is growing to the last recommended treatment for gonorrhea.
The report calls for state and local health departments to reprioritize rapid detection and treatment for people living in areas hardest hit by STDs. It also calls on providers to make STD screening and timely treatment a regular part of care, especially for pregnant women and MSM.
All three of the most common STDs can be cured with antibiotics. If left untreated, however, STD can trigger infertility, ectopic pregnancy, stillbirth, and higher risk for HIV transmission.
Article – All Rights Reserved.
Provided by FeedSyndicate