Antonio Manaytay – Fourth Estate Contributor
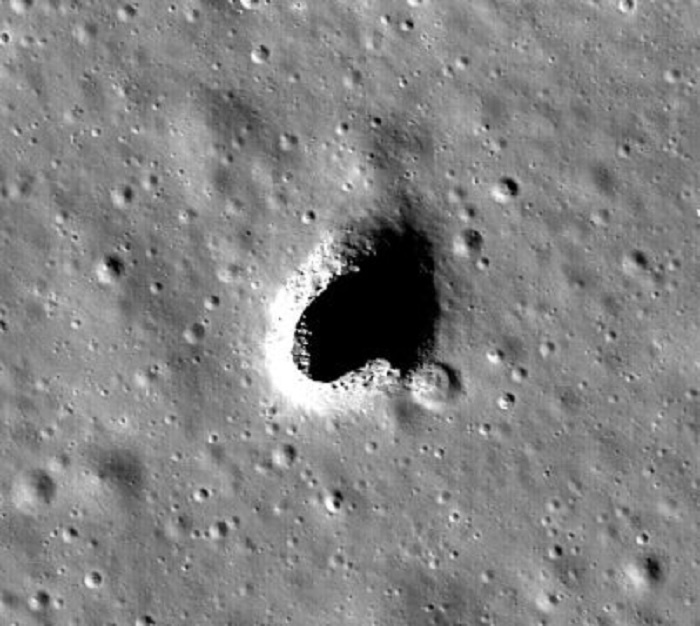
West Lafayette, IN, United States (4E) – The Moon could possibly be liveable, in spite of everything, actually as scientists have found its delicate spot – a big lava tube within the Marius Hills area. This area may function a pure human habitat past the hazardous circumstances of the lunar floor.
The Moon has no ambiance or magnetosphere to defend its inhabitants. Even house fits are usually not sufficient to guard astronauts from the dangerous radiation coming from the solar, excessive temperature, and meteorite impacts.
The most secure place, in accordance with the research revealed in Geophysical Research Letters, for human habitation to thrive is the cavernous lunar lava tube. Lava tubes are hole voids shaped when a flowing lava hardens an thickens above the stream of the flowing lava.
“It’s important to know where and how big lunar lava tubes are if we’re ever going to construct a lunar base,” senior researcher Junichi Haruyama of Japan’s house company JAXA, mentioned.
Analyzing the information from SELENE spacecraft the JAXA scientists had detected a definite echo sample close to the Marius Hills Skylight, which suggests the existence of a lava tube. The researchers had additionally discovered comparable echo patterns on the different websites of the moon, a sign that there could possibly be multiple lava tube.
SELENE’s radar system, nevertheless, was not constructed to detect lava tubes. This explains why it can not fly near the moon’s floor to additional validate the data and decide what’s contained in the tube.
The Japanese researchers enlisted the assistance of NASA’s GRAIL mission, which collects knowledge concerning the moon’s gravitational subject. They surveyed the areas recognized by GRAIL as areas with much less mass underneath the lunar floor. It helped them to sift via the volumes of knowledge they should analyze.
“They (JAXA scientists) knew about the skylight in the Marius Hills, but they didn’t have any idea how far that underground cavity might have gone,” GRAIL co-investigator Jay Melosh mentioned. Melosh can also be a distinguished professor of Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary Sciences at Purdue University.
“Our group at Purdue used gravity data over that area to infer that the opening was part of a larger system,” Melosh defined.
“By using this complimentary technique of radar, they were able to figure out how deep and high the cavities are,” he added.
Lava tubes additionally exist on Earth however smaller when in comparison with the lunar lava tubes.
Lava tubes may solely be detected by gravity knowledge if these tubes have a number of kilometers in size and a minimum of a kilometer in top and width. The knowledge from GRAIL mission clearly counsel that these lunar lava tubes are large enough for the gravity knowledge to detect, which signifies that the lava tube close to Marius Hills area is large enough to accommodate the biggest cities of the United States.
The findings may spark renewed pursuits to colonize the moon as a substitute of Mars.
Article – All Rights Reserved.
Provided by FeedSyndicate