Antonio Manaytay – Fourth Estate Contributor
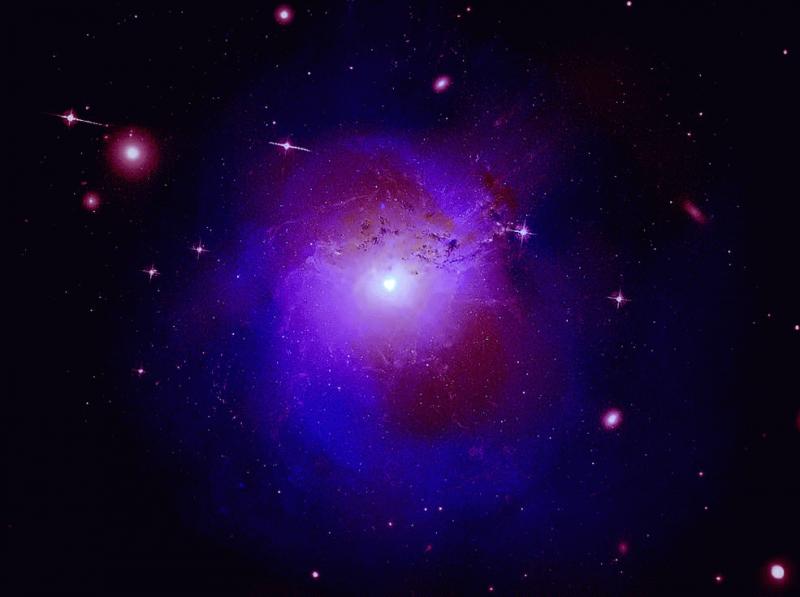
Cambridge, MA, United States (4E) – A brand new rationalization for a set of X-ray information from NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory, ESA’s XMM-Newton and a Japanese X-ray telescope Hitomi could have been a step in the correct route to lastly perceive the character of the darkish matter within the universe.
The astronomers, in a examine revealed on December 19 in Physical Review D, mentioned the X-ray information of a cluster of galaxies had proven a rise of depth of vitality of the new fuel at three.5 kiloelectron Volt (keV) within the Perseus galaxy cluster utilizing Chandra and XMM-Newton.
The astronomers led by Esra Bulbul from the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics in Cambridge, Massachusetts had additionally noticed the identical spike of depth in a examine of 73 different galaxy clusters utilizing XMM-Newton.
Another workforce led by Alexey Boyarsky of Leiden University within the Netherlands had additionally reported the identical spike: three.5 keV in galaxy M31 and the area on the fringe of Perseus cluster.
This noticed emission line, if confirmed by different observations, might assist advance the understanding of the mysterious and invisible substance generally known as darkish matter, which includes about 85 p.c of the universe.
“We expect that this result will either be hugely important or a total dud,” examine lead Joseph Conlon of Oxford University mentioned.
He mentioned there isn’t any center floor when “looking for answers to one of the biggest questions in science.”
The debate across the noticed emission line heightened when Hitomi did not detect the three.5 keV line in Perseus cluster. The Japanese telescope is designed to watch detailed options of X-ray spectra of cosmic origin.
“One might think that when Hitomi didn’t see the 3.5 keV line that we would have just thrown in the towel for this line of investigation,” examine co-author Francesca Day mentioned.
“On the contrary, this is where, like any good story, an interesting plot twist occurred,” she added.
The Hitomi telescope, Conlon and his workforce famous, had much less clear photographs than Chandra. Its information about Perseus cluster, due to this fact, are composed of a mix of X-ray alerts from a subtle element of sizzling fuel enveloping the galaxy within the heart and one other X-ray emission close to the monster black gap on this galaxy.
Chandra, with its sharp imaginative and prescient, might separate the contribution from these two sources. This impressed Bulbul and his colleagues to isolate the X-ray sign from the new fuel eradicating recognized sources of their evaluation, which embody X-rays coming from the monster black gap.
The Oxford workforce had discovered a deficit as an alternative of a surplus of X-rays at three.5 keV after they analyzed once more the 2009 Chandra information near the black gap on the heart of Perseus cluster. This discovering suggests: these X-rays at three.5 keV are absorbed in Perseus.
Simulating the Hitomi spectrum, the scientists discovered no hint of the entire spectrum of both absorption or emission of X-rays at three.5 keV.
For the Oxford scientists, the problem is tips on how to clarify why the absorption of X-ray mild was detected when observing the black gap and detecting the emission of X-ray mild at three.5 keV when wanting on the sizzling fuel away from the black gap.
This conduct is frequent for astronomers when observing stars and clouds of fuel utilizing optical telescopes. When enveloped by a cloud of fuel, the sunshine of a star exhibits absorption traces when the atoms within the fuel cloud absorbed the vitality of starlight. The absorption excites the atoms kicking off their vitality degree from low to excessive then return to a low degree with the emission of sunshine of a selected vitality. Then the sunshine is subtle which produced a web lack of mild or absorption line on the specific vitality within the seen spectrum of the star.
At the identical, observing a cloud of fuel away from the star would result in the detection of re-emitted mild as an emission line.
Conlon and his workforce proposed that particles of the darkish matter are like atoms having two vitality states separated by three.5 keV. Interpreted on this method, an absorption line at three.5 keV might be detected when observing close to the black gap and an emission line of the identical vitality is noticed when observing the new fuel away from the black gap.
“This is not a simple picture to paint, but it’s possible that we’ve found a way to both explain the unusual X-ray signals coming from Perseus and uncover a hint about what dark matter actually is,” examine co-author Nicholas Jennings mentioned.
Article – All Rights Reserved.
Provided by FeedSyndicate