This story additionally ran on NBC News. This story will be republished totally free (details).
Some hospitals try a curious new tactic to draw sufferers: free hernia screenings.
One Illinois hospital raffled off tickets for a smart speaker to entice folks to get their abdomens checked by a surgeon, whereas an Indiana hospital provided an opportunity to win dinner at a chophouse.
Announcements for screening occasions in Colorado and Maryland warned about “life-threatening” issues that would come up if hernias are left untreated. And hospitals in Georgia and California included an opportunity to “test-drive” a surgical robotic.
Hospitals say such screenings present useful schooling about remedy choices for the frequent medical situation, wherein a part of the gut protrudes by means of a weak spot within the belly wall.
But no analysis has been completed on hernia screenings, and a few consultants fear that these outreach efforts — a few of which showcase da Vinci robotic surgical procedure gadgets made by Intuitive Surgical primarily based in Sunnyvale, Calif. — could lead on folks to get probably dangerous operations they don’t want.
“My question is: Why are we doing this?” mentioned University of Michigan Medical School affiliate professor Dr. Dana Telem, the director of Michigan Medicine’s Comprehensive Hernia Program. “Even with the best intent, it makes me worry about the unintended consequences down the line.”
Email Sign-Up
Subscribe to KHN’s free Morning Briefing.
A Common Condition
An estimated 1.6 million groin hernias are recognized and 500,000 are surgically repaired yearly within the U.S., in keeping with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Some 27% of males and three% of girls are anticipated to have a groin hernia — the commonest kind — throughout their lifetimes.
Hernias could cause ache and irregular bulges, and plenty of sufferers finally choose to get them mounted with surgical procedure. Surgery may also stop a uncommon however severe situation known as strangulation, wherein a hernia can entrap the gut and minimize off blood circulate, requiring emergency surgical procedure.
However, issues from hernia surgical procedure are frequent. While any surgical procedure carries dangers, corresponding to an infection, groin hernia repairs go away as many as 12% of sufferers with persistent ache that may be debilitating, in keeping with a 2016 examine.
There’s additionally good proof that individuals who have few signs can safely go for watchful waiting moderately than go below the knife, in keeping with a 2018 article in JAMA. But such cautionary info is usually lacking in hospital screening bulletins.
In reality, consultants, together with the American College of Surgeons, say there’s no knowledge to again the usage of such hernia screenings.
“A screening for hernia? That makes no sense to me,” mentioned Dr. Michael Rosen, director of the Cleveland Clinic’s Hernia Center and medical director of the Americas Hernia Society Quality Collaborative, a consortium that tracks remedy outcomes. “Obviously, it’s just there to drive people to the operating room.”
Promoting Robotic Surgery
Some hospitals say warnings in regards to the dangers of letting hernias go untreated are applicable, and these occasions educate the general public, quell fears about robotic surgical procedure and serve individuals who in any other case can’t or received’t see a health care provider. Several hospitals mentioned their docs inform sufferers about all remedy choices, not simply robotic surgical procedure.
“Unfortunately, you can get people in the door for their own protection with the word ‘free,’” mentioned Victoria Montei, system director of surgical providers at Midland-based MidMichigan Health system, which has hosted two hernia screening occasions that attracted 52 folks and detected 33 hernias. “For a lot of people, a $20, $50, $100 copay [to see a doctor] can be a lot. They put it off.”
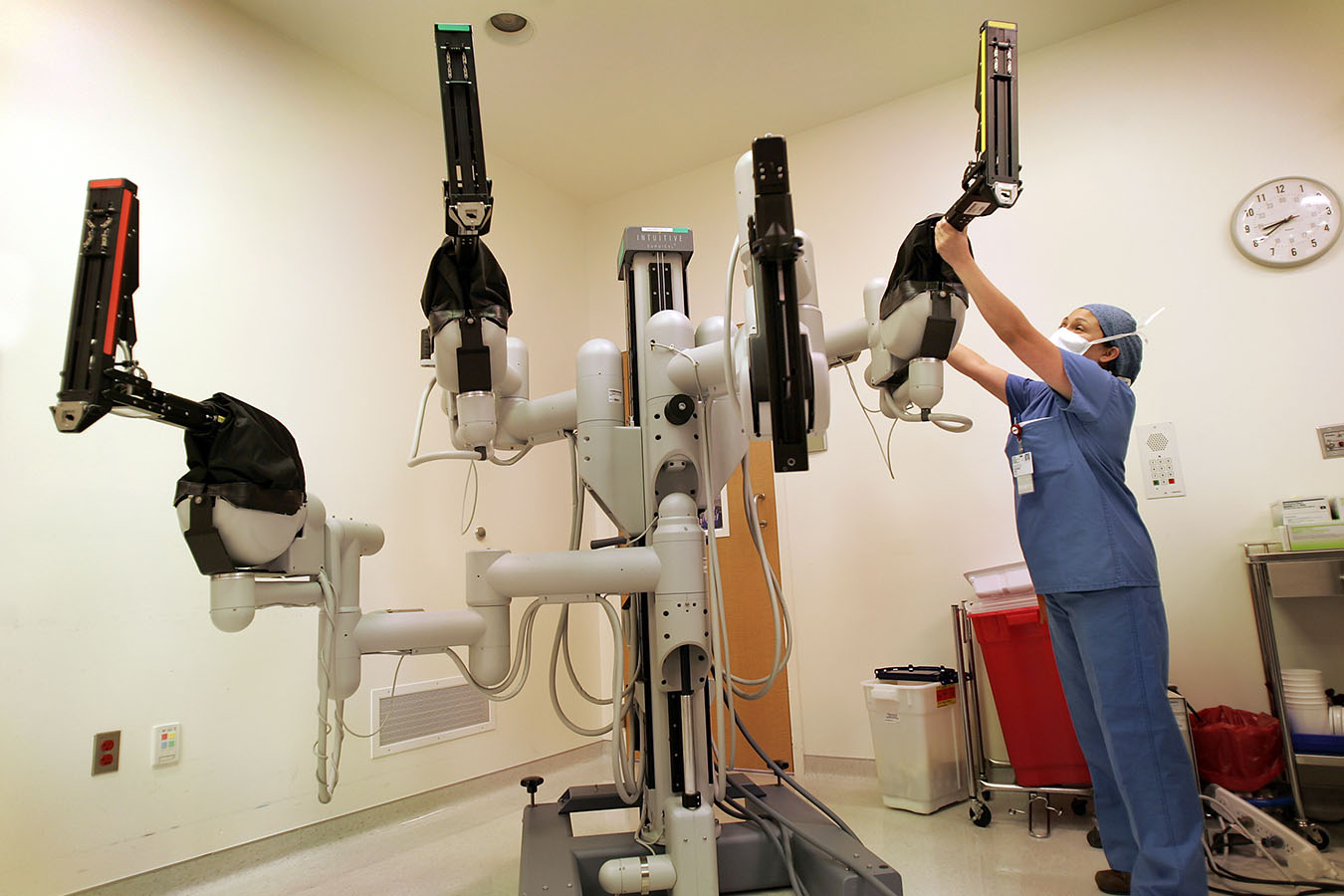
Some hospitals additionally use hernia screening to point out off their flashy da Vinci surgical robots, usually claiming that the robots’ 3D imaging and precision actions result in diminished ache, fewer complications and sooner restoration occasions.
Northeast Georgia Health System in Gainesville lately took certainly one of its 4 da Vinci gadgets out of fee for 3 days to demo it at a hernia screening and different group occasions. Seeing the da Vinci up shut “helps explain to the patient the value of it,” mentioned Health System spokeswoman Kristin Grace.
Yet some hospitals appear to be rethinking their methods. Dr. Sari Nabulsi, the chief medical officer of Medical Center Hospital in Odessa, Texas, which hosted a hernia screening occasion in 2018, mentioned by way of e-mail that the hospital “does not promote screening for hernia as there is no clinical value to such tests.” Its 2018 occasion was for “awareness” and the hospital “does not anticipate repeating the event in 2019,” he added.
Ben Drew, a spokesman for Walnut Creek, Calif.,-based John Muir Health, which marketed a robotic take a look at drive as a part of a hernia screening occasion, mentioned in an e-mail that the robotic was “not the focus of the assessment or the information provided to patients” and its announcement “could have been worded more clearly.”
Unclear Outcomes
The robotic has been marketed as a approach for surgeons so as to add minimally invasive surgical procedure to their toolkits. Most hernias are repaired by open surgical procedure, which makes use of giant cuts. Conventional laparoscopic surgical procedure, which makes use of smaller cuts, is technically difficult to study for hernia restore, Rosen mentioned.
But consultants say there’s no agency proof that robotic surgical procedure offers higher outcomes for hernia restore.
In reality, robotic surgical procedure has typically been adopted forward of proof that it provides a profit. Claims haven’t panned out for hysterectomies, and the Food and Drug Administration has issued a safety notice about the usage of robots in most cancers surgical procedures.
A screening for hernia? That is mindless to me. Obviously, it’s simply there to drive folks to the working room.
Dr. Michael Rosen, director of the Cleveland Clinic’s Hernia Center
Results of a pilot randomized clinical trial to match robotic hernia restore with standard laparoscopic surgical procedure are anticipated to be revealed this fall, mentioned Rosen, who’s main the examine.
The trial will evaluate the 2 approaches on patient-reported ache, price, ergonomics for surgeons and long-term recurrence charges. Still, bigger research shall be wanted to information medical follow, leaving solutions years away, mentioned Rosen.
Nevertheless, da Vinci’s producer, Intuitive Surgical, has been urgent forward with efforts to advertise its use for hernia restore. In an e-mail, Intuitive confirmed it has supplied demo robots and “educational information” for hernia screenings on the request of surgeons and hospitals.
The firm mentioned the data it offers for screening occasions consists of “descriptions of surgical and non-surgical options for hernia repair, including associated risks and benefits,” and it expects that “a large portion of hernia repairs will continue to be performed via different surgical modalities.” In different phrases, the way in which they’ve historically been completed.
Intuitive’s 2018 annual report recognized hernia restore as a “significant” development alternative, with normal surgical procedures, together with hernia restore, turning into the most important class of U.S. procedures in 2018. The firm reported internet earnings of $1.1 billion in 2018, up from $671 million in 2017.
The Economics Of Robotic Surgery
General surgical procedure is a mainstay of group hospitals, which have lately begun to put money into robotic methods as a solution to market themselves as “up on the latest technology,” mentioned Diane Robertson, director of well being expertise evaluation at ECRI Institute, a nonprofit that research security and cost-effectiveness of medical interventions.
But ECRI wrote an advisory warning that hospitals’ fast adoption of robotic methods has outpaced the event of coaching and credentialing requirements for the surgeons who use them.
Hospitals might not be interested by whether or not it’s greatest for the affected person or essentially the most cost-effective possibility, Robertson added. For hernia repairs, she mentioned, “There’s a huge question about why you would need to do them robotically.”
Each da Vinci prices a mean of $1.5 million, plus lots of of 1000’s of yearly to keep up and equip, in keeping with Intuitive’s annual report.
Intuitive advertises in a video on its web site that the robotic methods assist hospitals woo surgeons and win market share. The web site says robotic packages might help hospitals grow to be “more efficient and cost effective.”
But robotic surgical procedures cost hospitals more to offer and infrequently are reimbursed by insurers on the identical charge as for standard laparoscopy, in keeping with some consultants. A review of 510 hernia repairs on the University of Virginia discovered that the median hospital price of a robotic hernia restore was $7,162, versus $four,527 for laparoscopic procedures and $four,264 for open surgical procedures.
Though particular person sufferers might not essentially pay extra for a robotic surgical procedure, Robertson mentioned, the expertise contributes to larger general well being care spending and should divert assets from different priorities. In addition, taxpayer-funded Medicare might find yourself reimbursing hospitals indirectly for robotic surgical procedures.
For at the least one hospital, robotic surgical procedure didn’t repay.
Fifty-bed Massena Memorial Hospital in upstate New York ended its robotic providers in June to assist slash an working deficit, in keeping with chief monetary officer Patrick Facteau.
The da Vinci didn’t enhance the hospital’s surgical quantity regardless of a advertising push that included free monthly hernia screenings, Facteau mentioned.
“Part of the sales pitch is, you’ll get extra surgical procedures and scale back prices,” he mentioned. “We didn’t really see that.”
Nor, he mentioned, did the da Vinci enhance the hospital’s surgical high quality measures or scale back lengths of keep. Most hernia procedures are already completed on an outpatient foundation.
The hospital — within the 12,000-person city of Massena, simply south of the St. Lawrence River — was paying about $500,000 a yr to lease a da Vinci and canopy upkeep and devices, he mentioned.
Unlike most hospitals, which have purchased their methods, Massena had the flexibleness to ditch its lease. “Once you purchase it, getting out of it is not so easy,” Facteau mentioned.
This story additionally ran on NBC News. This story will be republished totally free (details). Related Topics Health Industry Hospitals Medical Devices