Phillip Reese
As summer season ushers in peak mosquito season, well being and vector management officers are bracing for the opportunity of one other yr of historic charges of dengue. And with local weather change, the dearth of an efficient vaccine, and federal analysis cuts, they fear the illness will develop into endemic to a bigger swath of North America.
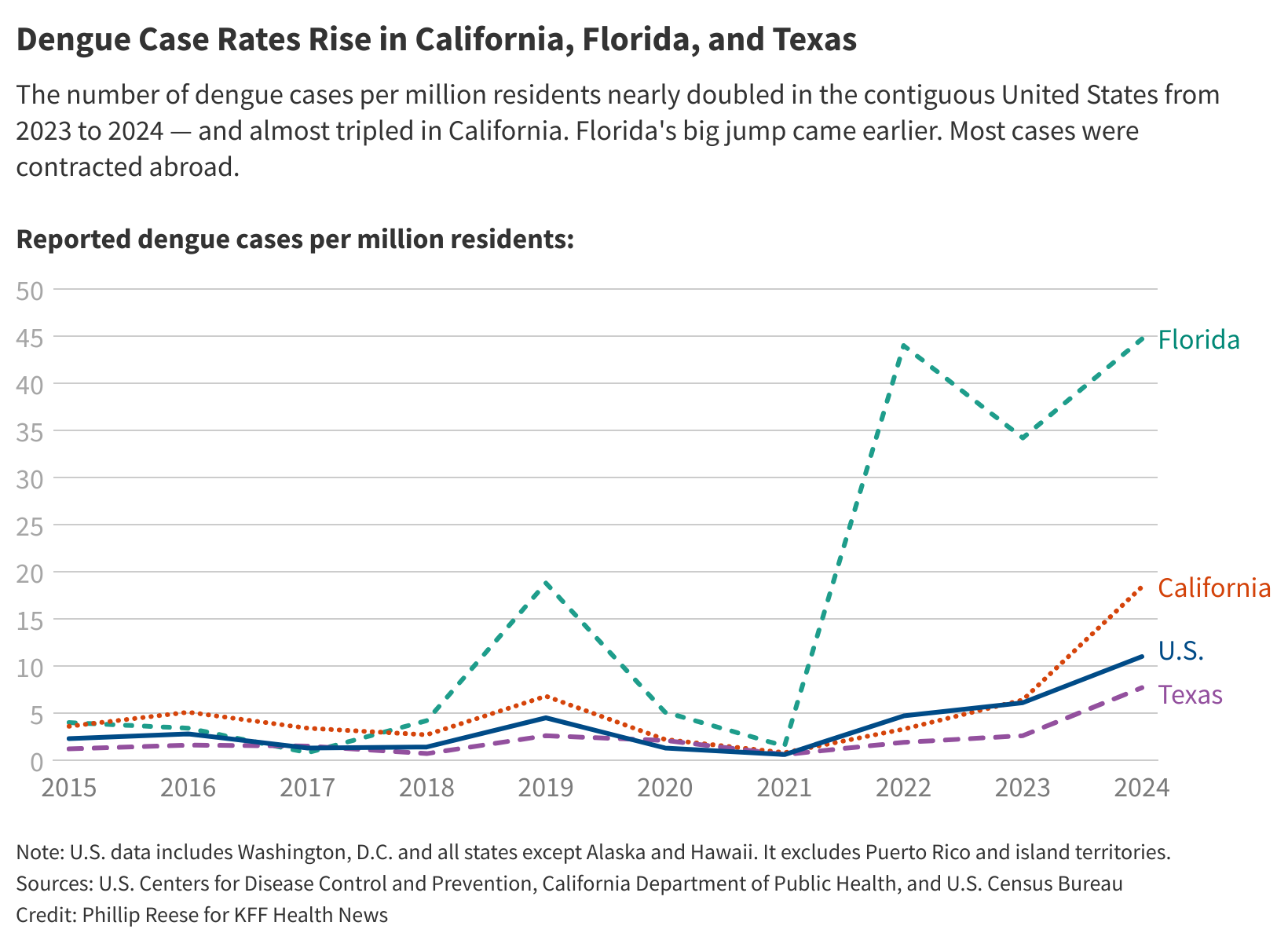
About 3,700 new dengue infections have been reported final yr within the contiguous United States, up from about 2,050 in 2023, in accordance with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. All of final yr’s circumstances have been acquired overseas, apart from 105 circumstances contracted in California, Florida, or Texas. The CDC issued a health alert in March warning of the continued threat of dengue an infection.
“I think dengue is here with us to stay,” mentioned infectious illness specialist Michael Ben-Aderet, affiliate medical director of hospital epidemiology at Cedars-Sinai in Los Angeles, about dengue changing into a brand new regular within the U.S. “These mosquitoes aren’t going anywhere.”
Dengue is endemic — a label well being officers assign when illnesses seem constantly in a area — in many warmer parts of the world, together with Latin America, India, and Southeast Asia. Dengue circumstances increased markedly last year in a lot of these locations, particularly in Central and South America.
The illness, which can spread when persons are bitten by contaminated Aedes mosquitoes, was not widespread within the contiguous United States for a lot of the final century. Today, most regionally acquired (which means unrelated to journey) dengue circumstances within the U.S. occur in Puerto Rico, which noticed a pointy enhance in 2024, triggering a neighborhood public well being emergency.
Most individuals who contract dengue don’t get sick. But in some individuals signs are extreme: bleeding from the nostril or mouth, intense abdomen ache, vomiting, and swelling. Occasionally, dengue causes loss of life.
California presents a case research in how dengue is spreading within the U.S. The Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus mosquitoes that transmit dengue weren’t recognized to be within the state 25 years ago. They are actually present in 25 counties and more than 400 cities and unincorporated communities, principally in Southern California and the Central Valley.
The unfold of the mosquitoes is regarding as a result of their presence will increase the chance of illness transmission, mentioned Steve Abshier, president of the Mosquito and Vector Control Association of California.
From 2016 by 2022, there have been a mean of 136 new dengue circumstances a yr in California, every case more than likely dropped at the state by somebody who had traveled and been contaminated elsewhere. In 2023, there have been about 250 new circumstances, together with two acquired regionally.
In 2024, California noticed 725 new dengue circumstances, together with 18 acquired regionally, state data shows.
Climate change might contribute to progress within the Aedes mosquitoes’ inhabitants, Ben-Aderet mentioned. These mosquitoes survive greatest in heat city areas, usually biting through the daytime. Locally acquired infections usually happen when somebody catches dengue throughout journey, then comes residence and is bitten by an Aedes mosquito that bites and infects one other individual.
“They’ve just been spreading like wildfire throughout California,” Ben-Aderet mentioned.
Dengue presents a problem to the numerous main care medical doctors who’ve by no means seen it. Ben-Aderet mentioned medical doctors who suspect dengue ought to acquire an in depth journey historical past from their sufferers, however confirming the analysis shouldn’t be all the time fast.
“There’s no easy test for it,” he mentioned. “The only test that we have for dengue is antibody tests.” He added that “most labs probably aren’t doing it commercially, so it’s usually like a send-out test from most labs. So you really have to suspect someone has dengue.”
Best practices for avoiding dengue embrace eliminating any standing swimming pools of water on a property — even small swimming pools — and utilizing mosquito repellent, Abshier mentioned. Limiting exercise at nightfall and daybreak, when mosquitoes chew most frequently, also can assist.
Efforts to fight dengue in California turned much more difficult this yr after wildfires ripped by Los Angeles. The fires occurred in a scorching spot for mosquito-borne sicknesses. San Gabriel Valley Mosquito and Vector Control District officers have worked for months to deal with greater than 1,400 unmaintained swimming swimming pools left within the wake of fireplace, eradicating potential breeding grounds for mosquitoes.
San Gabriel vector management officers have used native and state sources to deal with the swimming pools, mentioned district spokesperson Anais Medina Diaz. They have utilized for reimbursement from the Federal Emergency Management Agency, which has not traditionally paid for vector management efforts following wildfires.
In California, vector management companies are sometimes primarily funded by native taxes and costs on property house owners.
Some officers are pursuing the novel methodology of releasing sterilized Aedes mosquitoes to scale back the issue. That might show efficient, however deploying the tactic in a lot of areas can be pricey and would require a large effort on the state degree, Abshier mentioned. Meanwhile, the federal authorities is pulling again on interventions: Several shops have reported that the National Institutes of Health will stop funding new local weather change-related analysis, which might embrace work on dengue.
This yr, reported charges of dengue in a lot of the Americas have declined significantly from 2024. But the development within the United States probably gained’t be clear till later within the yr, after the summer season mosquito season ends.
Health and vector management researchers aren’t positive how unhealthy it is going to get in California. Some say there could also be restricted outbreaks, whereas others predict dengue might get a lot worse. Sujan Shresta, a professor and infectious illness researcher on the La Jolla Institute for Immunology, mentioned different locations, like Nepal, skilled comparatively few circumstances of dengue within the current previous however now usually see giant outbreaks.
There is a vaccine for kids, but it surely faces discontinuation from an absence of worldwide demand. Two different dengue vaccines are unavailable within the United States. Shresta’s lab is tough at work on an effective, safe vaccine for dengue. She hopes to launch outcomes from animal testing in a yr or so; if the outcomes are optimistic, human trials could possibly be potential in about two years.
“If there’s no good vaccine, no good antivirals, this will be a dengue-endemic country,” she mentioned.
Phillip Reese is a knowledge reporting specialist and an affiliate professor of journalism at California State University-Sacramento.
This article was produced by KFF Health News, which publishes California Healthline, an editorially impartial service of the California Health Care Foundation.
KFF Health News is a nationwide newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about well being points and is without doubt one of the core working packages at KFF—an impartial supply of well being coverage analysis, polling, and journalism. Learn extra about KFF.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story might be republished without cost (details).