Paula Span and Oona Zenda
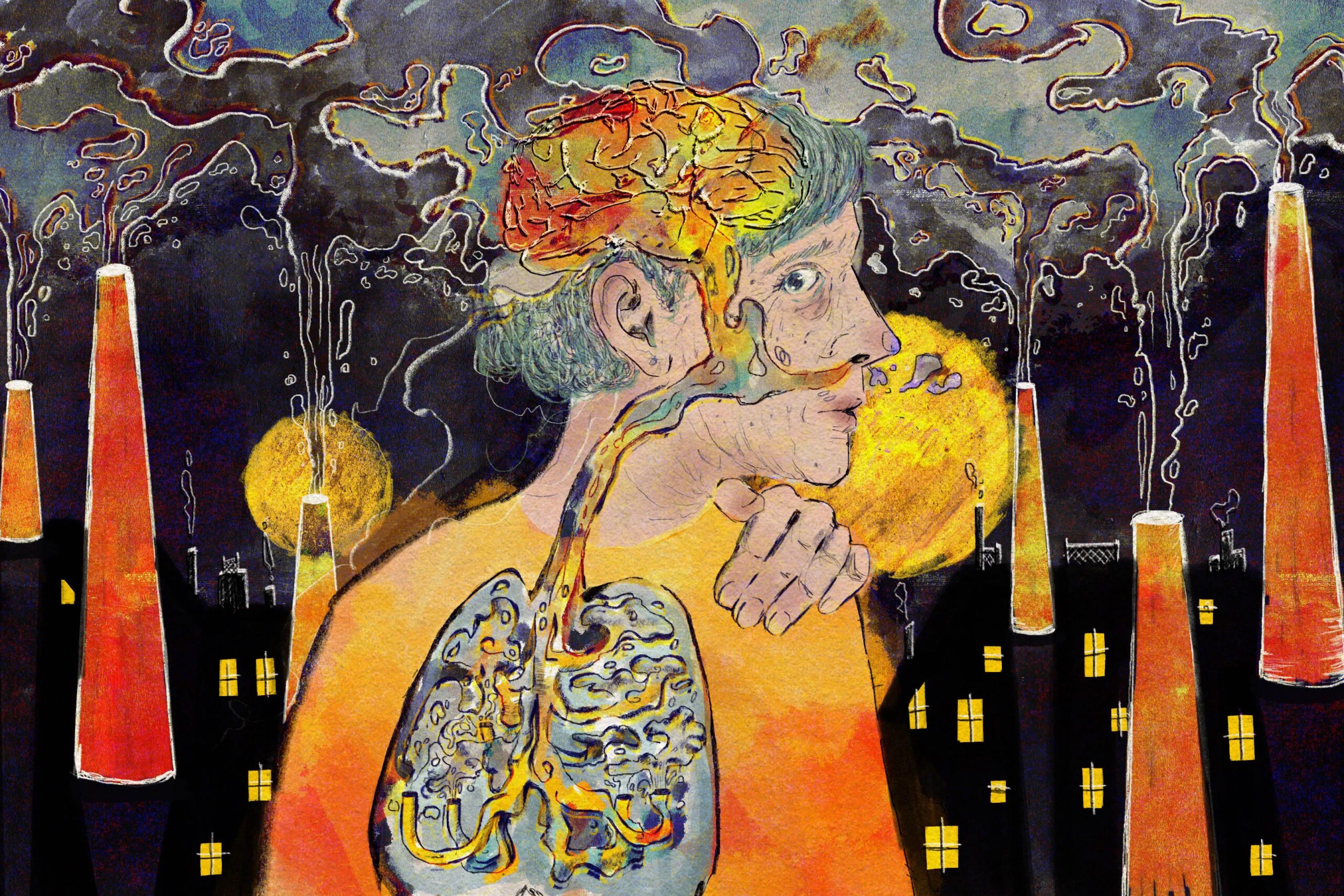
Illustration by Oona Zenda
For years, the 2 sufferers had come to the Penn Memory Center on the University of Pennsylvania, the place medical doctors and researchers observe folks with cognitive impairment as they age, in addition to a bunch with regular cognition.
Both sufferers, a person and a girl, had agreed to donate their brains after they died for additional analysis. “An amazing gift,” mentioned Edward Lee, the neuropathologist who directs the brain bank on the college’s Perelman School of Medicine. “They were both very dedicated to helping us understand Alzheimer’s disease.”
The man, who died at 83 with dementia, had lived within the Center City neighborhood of Philadelphia with employed caregivers. The post-mortem confirmed giant quantities of amyloid plaques and tau tangles, the proteins related to Alzheimer’s illness, spreading by means of his mind.
Researchers additionally discovered infarcts, small spots of broken tissue, indicating that he had suffered a number of strokes.
By distinction, the girl, who was 84 when she died of mind most cancers, “had barely any Alzheimer’s pathology,” Lee mentioned. “We had tested her year after year, and she had no cognitive issues at all.”
The man had lived a couple of blocks from Interstate 676, which slices by means of downtown Philadelphia. The lady had lived a couple of miles away within the suburb of Gladwyne, Pennsylvania, surrounded by woods and a rustic membership.
The quantity of air air pollution she was uncovered to — particularly, the extent of superb particulate matter referred to as PM2.5 — was lower than half that of his publicity. Was it a coincidence that he had developed extreme Alzheimer’s whereas she had remained cognitively regular?
With growing proof that power publicity to PM2.5, a neurotoxin, not solely damages lungs and hearts however can also be related to dementia, in all probability not.
“The quality of the air you live in affects your cognition,” mentioned Lee, the senior writer of a latest article in JAMA Neurology, one among a number of giant research prior to now few months to display an affiliation between PM2.5 and dementia.
Scientists have been monitoring the connection for at the very least a decade. In 2020, the influential Lancet Commission added air pollution to its checklist of modifiable danger elements for dementia, together with widespread issues like listening to loss, diabetes, smoking, and hypertension.
Yet such findings are rising when the federal authorities is dismantling efforts by earlier administrations to proceed decreasing air air pollution by shifting from fossil fuels to renewable vitality sources.
“‘Drill, baby, drill’ is totally the wrong approach,” mentioned John Balmes, a spokesperson for the American Lung Association who researches the consequences of air air pollution on well being on the University of California-San Francisco.
“All these actions are going to decrease air quality and lead to increasing mortality and illness, dementia being one of those outcomes,” Balmes mentioned, referring to latest environmental strikes by the White House.
Many elements contribute to dementia, after all. But the function of particulates — microscopic solids or droplets within the air — is drawing nearer scrutiny.
Particulates come up from many sources: emissions from energy vegetation and residential heating, manufacturing facility fumes, motorcar exhaust, and, more and more, wildfire smoke.
Of the a number of particulate sizes, PM2.5 “seems to be the most damaging to human health,” Lee mentioned, as a result of it’s among the many smallest. Easily inhaled, the particles enter the bloodstream and flow into by means of the physique; they will additionally journey immediately from the nostril to the mind.
The analysis on the University of Pennsylvania, the biggest post-mortem research up to now of individuals with dementia, included greater than 600 brains donated over twenty years.
Previous analysis on air pollution and dementia principally relied on epidemiological research to determine an affiliation. Now, “we’re linking what we actually see in the brain with exposure to pollutants,” Lee mentioned, including, “We’re able to do a deeper dive.”
The research individuals had undergone years of cognitive testing at Penn Memory. With an environmental database, the researchers have been in a position to calculate their PM2.5 publicity based mostly on their residence addresses.
The scientists additionally devised a matrix to measure how severely Alzheimer’s and different dementias had broken donors’ brains.
Lee’s workforce concluded that “the higher the exposure to PM2.5, the greater the extent of Alzheimer’s disease,” he mentioned. The odds of extra extreme Alzheimer’s pathology at post-mortem have been nearly 20% better amongst donors who had lived the place PM2.5 ranges have been excessive.
Another analysis workforce lately reported a connection between PM2.5 publicity and Lewy physique dementia, which incorporates dementia associated to Parkinson’s illness. Generally thought-about the second most typical sort after Alzheimer’s, Lewy physique accounts for an estimated 5% to fifteen% of dementia instances.
In what the researchers consider is the biggest epidemiological research up to now of air pollution and dementia, they analyzed information from greater than 56 million beneficiaries with conventional Medicare from 2000 to 2014, evaluating their preliminary hospitalizations for neurodegenerative illnesses with their publicity to PM2.5 by ZIP codes.
“Chronic PM2.5 exposure was linked to hospitalization for Lewy body dementia,” mentioned Xiao Wu, an writer of the research and a biostatistician on the Mailman School of Public Health at Columbia University.
After controlling for socioeconomic and different variations, the researchers discovered that the speed of Lewy physique hospitalizations was 12% larger in U.S. counties with the worst concentrations of PM2.5 than in these with the bottom.
To assist confirm their findings, the researchers nasally administered PM2.5 to laboratory mice, which after 10 months confirmed “clear dementia-like deficits,” senior writer Xiaobo Mao, a neuroscientist on the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, wrote in an e mail.
The mice acquired misplaced in mazes that they’d beforehand dashed by means of. They had earlier constructed nests shortly and compactly; now their efforts have been sloppy, disorganized. At post-mortem, Mao mentioned, their brains had atrophied and contained accumulations of the protein related to Lewy our bodies in human brains, referred to as alpha-synuclein.
A third analysis, printed this summer season in The Lancet, included 32 research performed in Europe, North America, Asia, and Australia. It additionally discovered “a dementia diagnosis to be significantly associated with long-term exposure to PM2.5” and to sure different pollution.
Whether so-called ambient air air pollution — the outside sort — will increase dementia due to irritation or different physiological causes awaits the subsequent spherical of analysis.
Although air air pollution has declined within the United States over twenty years, scientists are calling for nonetheless stronger insurance policies to advertise cleaner air. “People argue that air quality is expensive,” Lee mentioned. “So is dementia care.”
President Donald Trump, nevertheless, reentered workplace vowing to extend the extraction and use of fossil fuels and to dam the transition to renewable vitality. His administration has rescinded tax incentives for photo voltaic installations and electrical autos, Balmes famous, including, “They’re encouraging continuing to burn coal for power generation.”
The administration has halted new offshore wind farms, introduced oil and gas drilling within the Arctic National Wildlife Refuge in Alaska, and moved to cease California’s plan to transition to electrical automobiles by 2035. (The state has challenged that motion in courtroom.)
“If policy goes in the opposite direction, with more air pollution, that’s a big health risk for older adults,” Wu mentioned.
Last 12 months, underneath the Biden administration, the Environmental Protection Agency set tougher annual standards for PM2.5, noting that “the available scientific evidence and technical information indicate that the current standards may not be adequate to protect public health and welfare, as required by the Clean Air Act.”
In March, the EPA’s new chairman announced that the company can be “revisiting” these stricter requirements.
The New Old Age is produced by means of a partnership with The New York Times.
KFF Health News is a nationwide newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about well being points and is among the core working applications at KFF—an unbiased supply of well being coverage analysis, polling, and journalism. Learn extra about KFF.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story will be republished without cost (details).