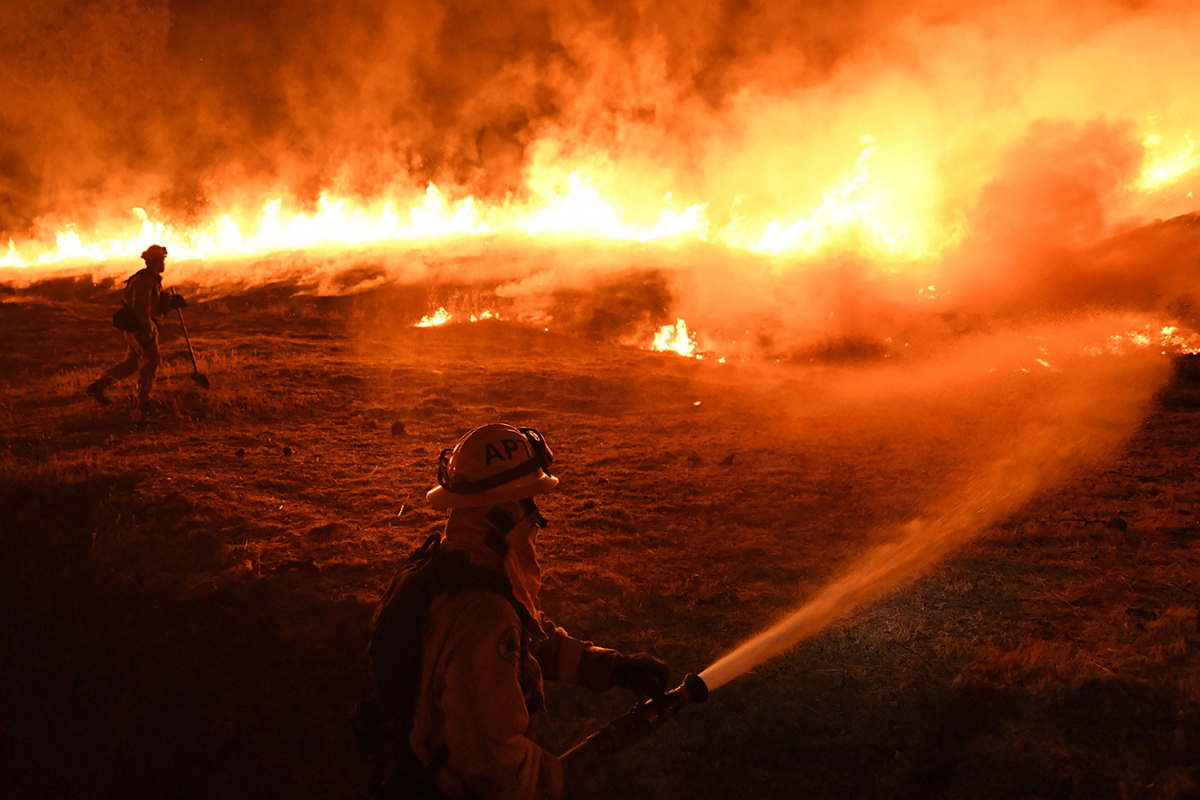
Debbie Dobrosky seen a peculiar hue within the sky on Monday — “a very ugly yellow casting” — as she peeked outdoors. A big cloud of smoke had begun to cowl the solar.
By Tuesday, the smoke was so heavy that “even inside my apartment I’ve had to use my inhaler twice this morning, which is not a normal thing,” mentioned Dobrosky, a Riverside County, Calif., resident who lives about 30 miles from a fast-growing hearth within the Cleveland National Forest.
“Today I’m stuck inside, there’s no going out,” mentioned Dobrosky, 67, who has power obstructive pulmonary illness (COPD), an inflammatory lung situation.
At least 17 giant fires are burning throughout California, destroying a whole lot of 1000’s of acres, sending poisonous pollution into the air and contaminating water provides. The air high quality in sure areas — notably close to the huge Mendocino Complex Fire within the northern a part of the state — is among the many worst officers have ever seen.
And situations aren’t anticipated to enhance as new blazes get away and others rage uncontrolled. With temperatures at occasions reaching into the triple digits, unpredictable winds and desiccated brush that serves as kindling, there’s no finish in sight to this 12 months’s hearth season.
Debbie Dobrosky, 67, of Glen Avon, Calif., has respiratory points and is afraid to go outdoors due to the thick smoke clouds flowing in from The Holy Fire in Southern California.
“We are in a situation now where the wildfire season doesn’t really have its normal beginning or end,” mentioned Lori Kobza, spokeswoman for the Sacramento Metropolitan Air Quality Management District.
The 629,000 acres burned this 12 months follows giant swaths torched final 12 months in Ventura, Santa Barbara, Napa and Sonoma counties, inflicting dozens of deaths, in keeping with the California Department of Forestry and Fire Protection. Many scientists attribute the extra frequent and ferocious fires within the U.S. and world wide, no less than partly, to climate change.
Meanwhile, air high quality districts across the state have issued warnings to remain indoors — with home windows shut and the air conditioner working — and to restrict out of doors actions. In many locations, youngsters’ ball video games, using classes and summer season camps have been cancelled.
NASA satellite photos present towers of smoke in California billowing into the ambiance. Up and down the state, air high quality officers have marked huge swaths as crimson with spots of purple — locations the place air is unhealthy or very unhealthy to breathe. Smoke and ash can journey dozens and even a whole lot of miles.
Children, older folks and people with respiratory sicknesses corresponding to bronchial asthma and COPD are notably susceptible to smoke-related well being issues. But otherwise-healthy folks additionally could expertise short-term respiratory issues, eye irritation and coughing.
Fine particulate matter, which is generally invisible, can result in irritation of the lungs and different organs. For folks with cardiac issues, poisonous smoke has been related to an elevated threat of coronary heart assaults, strokes and demise, mentioned Dr. Michael Schivo, affiliate professor of medication at University of California-Davis.
Schivo, who has lived within the Sacramento space most of his life, mentioned he can’t keep in mind the air being as dangerous as up to now few years. More sufferers with power lung illness are experiencing extra uncontrolled signs, he mentioned.
Lisa Suennen, 52, who lives in Marin County, about 100 miles from the Mendocino hearth, has gone to the physician 3 times in current weeks due to lingering respiratory points. She mentioned her downside began as a chilly, however because the air bought worse, she developed bronchitis and her bronchial asthma flared up. “My lungs do not feel healthy right now,” she mentioned. “It is just not natural to breathe.”
Air high quality consultants and physicians mentioned extra fires are sure to happen, and other people with well being points must have a plan for the dangerous air days, corresponding to retaining further drugs readily available. “This isn’t the first fire season California has had and it won’t be the last,” mentioned Patrick Chandler, spokesman for the South Coast Air Quality Management District. “You can’t really tough this out.”
Heavy smoke is seen from Debbie Dobrosky’s condominium in Glen Avon, Calif. Even although she has stayed indoors, she has sore lungs and says respiratory has develop into a chore.
Some folks say they haven’t any selection however to take dangers. Alyssa Mayo, 31, who has struggled with respiratory points for twenty years, runs a rehabilitation middle for horses and canine northeast of Sacramento. Now, she will’t see the mountain vary out her window due to the smoke.
But Mayo mentioned she has horses and canine to take care of. “Unfortunately, with our business, we can’t sit inside all day,” she mentioned. “I wish I could hunker down and stay out of it, but these animals depend on us.”
Air high quality would be the most urgent challenge, however scientists say that finally water — one other human necessity — is at risk, too. Ash, burned soil and poisonous residue from incinerated homes, companies and equipment could make their method into lakes, rivers and reservoirs, mentioned Carmen Burton, a hydrologist with the U.S. Geological Survey’s California Water Science Center in San Diego. The extent of the contamination relies on elements corresponding to topography and the quantity and sort of supplies burned.
Wildfires usually sweep by rural areas greater than city — and this 12 months follows that sample, mentioned Catherine Dunwoody, chief of the monitoring and laboratory division for California’s Air Resources Board. Dunwoody cited among the mountainous areas in and round Yosemite, specifically, the place a 94,000-acre hearth was considerably contained as of Tuesday afternoon.
Yet as housing complexes encroach on wild lands, residents more and more threat their properties, their well being and even their lives.
Some components of the state endure greater than others. The complete San Joaquin Valley faces the unwell results of blazes not solely in close by Yosemite however all through Northern California, mentioned Anthony Presto, a spokesman for the San Joaquin Valley Air Pollution Control District. This area, he defined, is surrounded on three sides by mountain ranges, making it simpler for pollution and smoke to funnel southward and develop into trapped in a bowl.
Kimberly McCoy, who lives in Fresno, has seen that firsthand. She and her son each have bronchial asthma, and she or he mentioned her chest feels tight and her son has been wheezing. McCoy mentioned she hasn’t let her son outdoor in current days. “That’s really hard for an active 6-year-old,” she mentioned.
In Sacramento County, smoke is now trapped below a ridge of excessive strain. Kobza, of the native air district, mentioned that if masks are worn, they need to be specialised to guard from the superb particulate matter. Dust masks from the ironmongery store gained’t reduce it, she mentioned.
“People have a false sense of security,” she mentioned. “If it’s small enough to get into the bloodstream, it’s small enough to get through paper.”
Some persons are carrying masks even of their vehicles. Dobrosky, of Riverside County, mentioned she lately ordered a pack of specialised masks from Amazon after working out throughout final 12 months’s blazes. After these fires, she additionally purchased a treadmill in order that she might train inside. Even so, Dobrosky mentioned, her lungs are sore.
“Breathing” she mentioned, “has become a chore.”
Alex Leeds Matthews and Stephanie O’Neill contributed to this story.