Use Our Content This story could be republished free of charge (details).
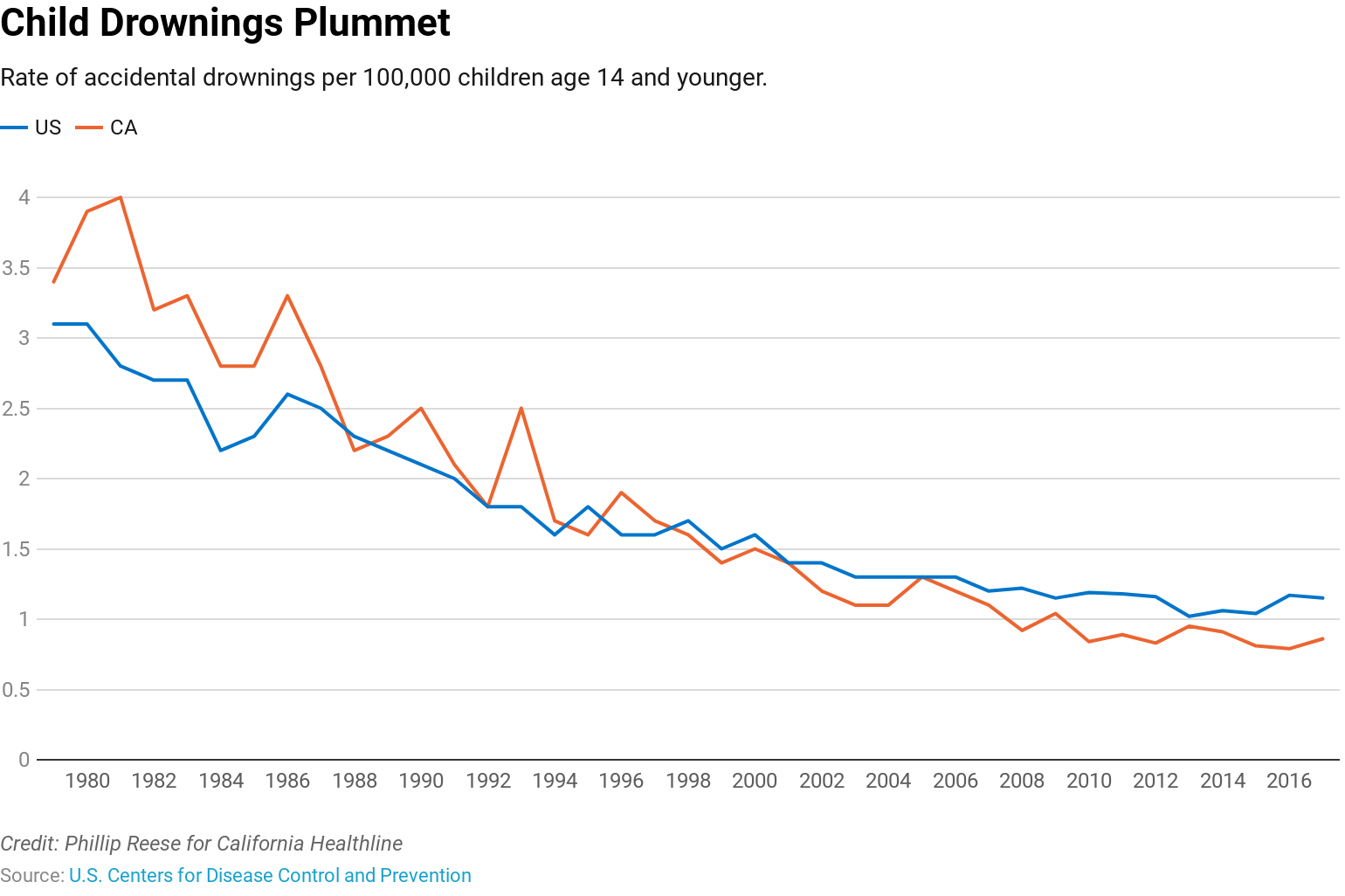
Some welcome information on the peak of summer season swimming season: Children are far much less prone to drown in California than they had been within the 1980s — and baby drowning charges have continued to fall even previously decade, in response to knowledge from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The nation as an entire has skilled an identical, although much less dramatic, decline, with drowning charges for youngsters age 14 and youthful now about one-third of what they had been within the early 1980s.
Experts say state and native legal guidelines that require extra fencing and security measures round household swimming swimming pools have made a distinction, together with elevated consciousness of the risks of letting younger youngsters swim alone.
From 1980 to 1982, 586 California youngsters age 14 and youthful died in unintended drownings, a rate of 3.7 deaths per 100,000 youngsters, federal knowledge present. The tempo fell sharply within the 1990s, to a price of about 1.4 deaths per 100,000 from 1999 to 2001. From 2015 to 2017, 186 youngsters drowned in California. That determine interprets to 0.8 drownings per 100,000 youngsters.
Email Sign-Up
Subscribe to KHN’s free Morning Briefing.
Nationally, the drowning price for youngsters age 14 and youthful was 2.9 per 100,000 over three years from 1980 to 1982 (four,417 deaths). By comparability, from 2015 to 2017, that price fell to 1.1 per 100,000 (2,051 deaths).
Despite the enhancements, drowning stays the nation’s main injury-related reason behind dying for youngsters ages 1 to four, and youngsters in that age group are most certainly to drown in a swimming pool quite than a pure physique of water. Highly publicized instances, just like the June dying of River Smith, the Three-year-old son of nation singer Granger Smith, are a reminder of the dangers. River drowned within the pool at his household’s Texas dwelling, whereas his father and siblings performed close by.
“Often drowning is silent; it occurs in 20 to 60 seconds,” mentioned Adam Katchmarchi, govt director of the National Drowning Prevention Alliance. “Parents don’t realize how quickly that can happen to their children.”
Nadina Riggsbee, founder and president of the California-based Drowning Prevention Foundation, mentioned the sharp decline in unintended drownings in California is a direct outgrowth of strict uniform constructing codes.
“We have the strongest, most stringent pool-fencing law in the nation, in the world, actually,” Riggsbee mentioned. “We suggest to other states: Why don’t you mirror the California law?”
Riggsbee’s 2-year-old-daughter died and her 14-month-old son was severely injured within the late 1970s when a babysitter briefly left the 2 unattended at their dwelling in San Ramon, a metropolis in Contra Costa County. The babysitter had uncared for to lock a sliding door after letting out the household canine, and the youngsters exited via the door to the pool.
A number of years later, Contra Costa County turned the primary county within the nation to cross a regulation requiring fencing round swimming pools, Riggsbee mentioned. She and different advocates pressed different communities to undertake related ordinances. Their best success got here within the late 1990s, when the state legislature handed the Swimming Pool Safety Act.
The statewide legislation requires that new swimming pools are accompanied by one of many following security options: a fence that separates the pool from a house; a strong pool security cowl; exit alarms on doorways main from the house to the pool space; self-closing and self-latching doorways main from the house to the pool space; or a security system as efficient as these 4 measures.
In 1995 and 1996, earlier than the legislation took impact, 269 California youngsters died from unintended drowning. By comparability, in 2016 and 2017, 125 California youngsters drowned — a drop of greater than 50%.
The legislation was amended within the mid-2000s to permit for 2 different forms of security measures: a pool alarm that sounds upon unauthorized entry into the water, or a detachable mesh pool fence with self-closing, self-latching doorways.
National security organizations proceed to push for extra states and cities to undertake uniform requirements and have embraced as a mannequin the International Swimming Pool and Spa Code. The code requires bodily boundaries round swimming pools and units requirements on gates and latches. So far, 21 states and greater than 180 native businesses have adopted the code, trade knowledge present.
Even with statewide requirements, baby drowning charges differ throughout California. Counties within the state’s arid Central Valley — identified for its lengthy, scorching summers — are inclined to have greater baby drowning charges than the remainder of the state.
“There are more days and months of heat,” Riggsbee mentioned. “The families are using the pools more frequently.”
Riggsbee and different advocates hope a California legislation enacted final yr will end in even fewer baby drownings in years to come back. Under the legislation, newly put in or reworked personal swimming pools should characteristic two security measures, quite than only one.
Phillip Reese is an information reporting specialist and an assistant professor of journalism at California State University-Sacramento.
Use Our Content This story could be republished free of charge (details).
This KHN story first printed on California Healthline, a service of the California Health Care Foundation.
Related Topics California Public Health States Children’s Health